class g airspace canada
Altitudes at 18000 feet MSL and above in Class A airspace are commonly referred to in hundreds of feet as Fight Levels abbreviated FL. In the SDA it begins at 18000.

Canadian Airspace Classes Coastal Drone
Class F airspace is specifically described in IFR en route charts as well as the Designated Airspace Handbook.
. How To Find It. Other types of airspace have special classifications that tell us what they are used for how they are used if and how they are controlled and what can be done in them. CY indicates that the.
Contol zones can be class B C D or E. Drone pilots with an Advanced Drone Pilot Certificate may enter other classes of airspace if they have permission from the authority managing the airspace NAV CANADA or DND as appropriate. The specific dimensions of Class B airspace in Canada can be found in the DAH Designated Airspace Handbook.
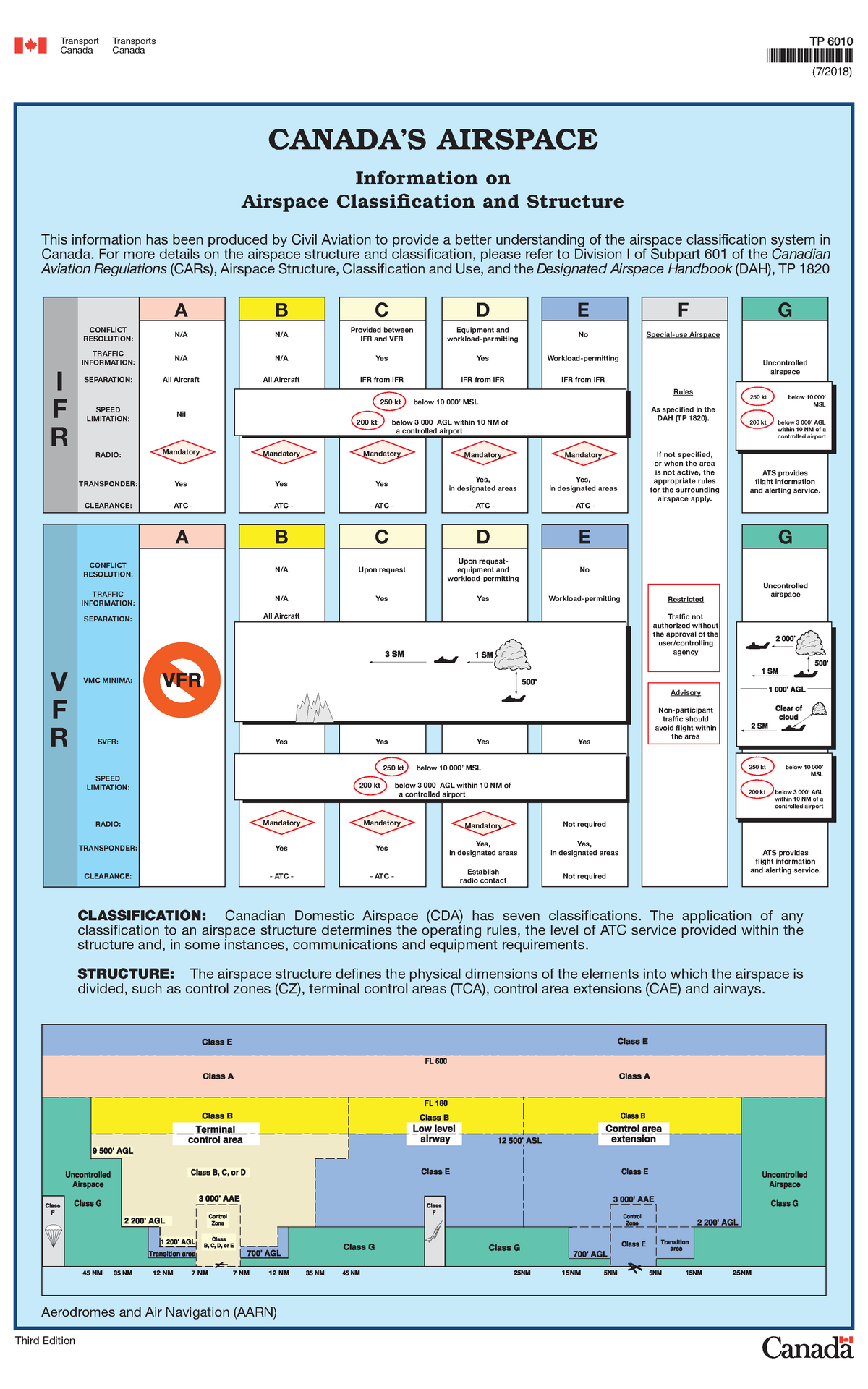
2 airspace that you have to talk to someone. There are seven classes of airspace in Canada and each is designated by a letter A through G. Yes it is possible to fly IFR in Class G airspace.
At and above FL 100. However there is Class F airspace in Canada generally reserved for special use airspace like restricted and alert areas. That is not otherwise designated Class B C or D airspace.
Controlled airspace classes C to E By Night. This is the airspace where. G F Uncontrolled airspace Restricted airspace.
This line shows enroute Class E airspace starting at. Drone pilots with a Basic Drone Pilot Certificate must stay in Class G. Class G airspace is most easily found on a sectional map when a fading thick blue line appears.
Class A airspace is everything from 18000ft MSL up to FL600 and only. The airspace classification system is a critical part of managing. Class G airspace is all airspace that is not another classification.
Canadian airspace is the region of airspace above the surface of the Earth within which Canada has jurisdiction. Airspace is managed by Transport Canada and detailed information regarding exact dimensions and classification is. Google Maps Viewer for Canadian Airspace.
It extends from the surface to the base of the overlying Class E airspace. Use of our national air traffic control ATC service is mandatory in Class A airspace that begins at 18000 feet MSL and extends upward to 60000 feet MSL. Class E is very similar to CLASS D.
The airspace structure defines the physical dimensions of the elements into which the airspace is divided such as control zones CZ terminal control areas TCA control area extensions CAE and airways. Tower at YBW. Class E airspace is similar to CLASS G with the difference being flights under 3000ft need to have sight of the surface and clear of cloud in Class G that nugget of info will probably be in your exam Below is another way to interporate Airspace classes.
It is what we call open airspace. VFR traffic must file a flight plan and request a route to enter. 8 km flight visibility 1500 m horizontally from cloud 1000 ft 300m vertically from cloud.
Show only when airspace is. 5 km flight visibility 1500 m horizontally from cloud 1000 ft 300m vertically from cloud Canada VFR minima Uncontrolled Airspace class G. Each restricted and advisory area within Canada has been assigned an identification code group which consists of the four following parts.
1 airspace that you dont have to talk to. And its always exclusive. The type of Class F airspace is indicated in the identifier published in charts of which the following is a typical example.
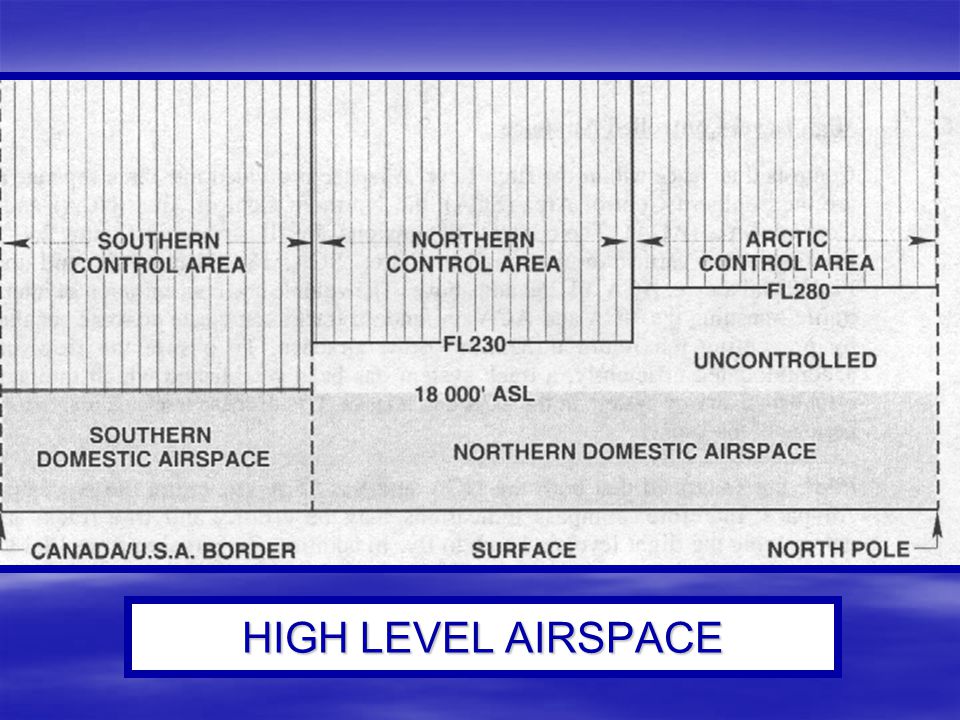
3 airspace that youre not allowed in at any time. The Arctic Control Area ACA and the Northern Control Area NCA. Class F Class G Fig 7-2 Canadian Airspace Structure.
The NDA is divided into two Control Areas. Any airspace not specifically identified as controlled airspace on a chart is Class G airspace. On a map Class Gs ceiling is the floor of Class E airspace.
It falls within a region roughly defined as either the Canadian land mass the Canadian Arctic or the Canadian archipelago and areas of the high seas. Class B airspace is generally defined as low level controlled airspace and exists between 12500 ft and the floor of Class A airspace but it may include some control zones and control areas that are lower. Special-use airspace for activities such as parachuting and aircraft testing.
Class A airspace exists exclusively between FL180 and FL600. CDAH - Canadian Designated Airspace Handbook Class A-G - Airspace in Canada is divided into 7 classes. For detailed information on terminal control areas TCAs control zones CZ and transition areas refer to the.
This information has been produced by Civil Aviation to provide a better understanding of the airspace classification system in Canada. Because of this requirement time spent. Class G airspace would exist from the ground up to a specific altitude say 2200 feet above the ground where the airspace then changes to controlled airspace such as.
Class A airspace Class A airspace is designated where an operational need exists to exclude VFR aircraft. Non-participating aircraft should avoid this area. However in the NDA it does not.
This is really not very hard to comprehend but. Though it may not seem like it Class G is most of Canadas airspace. Two-way radio communication is required.
When operating in Class A B C or D airspace. No aircraft may enter without permission from the user agency or controlling agency. For example if Class E starts at 700 feet AGL Class G goes up to but doesnt include 700 feet AGL.
For example flight level two zero zero or FL. 14 CFR 91177 requires pilots to remain at least 1000ft above the highest obstacle within a horizontal distance of 4NM from the course indicated in the filed flight plan. Canadian domestic airspace is divided into 7 classes.
Class G is your uncontrolled airspace. It includes all controlled low-level airspace between 12500 and up to but not including 18000. While theres no one to coordinate with for airspace permission in class G there can still be MF and ATF aerodromes that you may needwant to communicate with.
Typically Class G airspace includes all of the airspace below 14500 ft. Much of Class G airspace in Canada exists directly below controlled airspace. Class A-G - Airspace in Canada is divided into 7 classes.
Class G airspace would exist from the. _____ Using 1234 MHz reserved for soaring operations as an air-to-air channel can cause problems in some areas. However pilots are required to meet IFR altitude and flight level requirements.
In class B airspace IFR and VFR traffic is allowed.
Canada S Airspace Transport Canada Transports Canada 7 2018 Third Edition Aerodromes And Air Studocu

Canadian Airspace Classes Coastal Drone

Is This Class G Airspace Aviation Stack Exchange

Helicopter Ground School Airspace Rotorworks Inc

How High Is Class G Uncontrolled Airspace In The Columbia Valley

Canadian Airspace Classifications Diagram Quizlet

Uncontrolled Airspace Archives Flytime Ca

2019 Canadian Airspace File Update Fly360

Canadian Airspace Classes Coastal Drone

Where Can I Fly My Drone A Primer On Canadian Airspace Coastal Drone

Canadian Airspace Classes Coastal Drone

Air Space Airspace And Airports Ppt Download

Flight Safety Checks Everything You Should Know Before You Takeoff Aerial Evolution Association Of Canada

Helicopter Ground School Airspace Rotorworks Inc